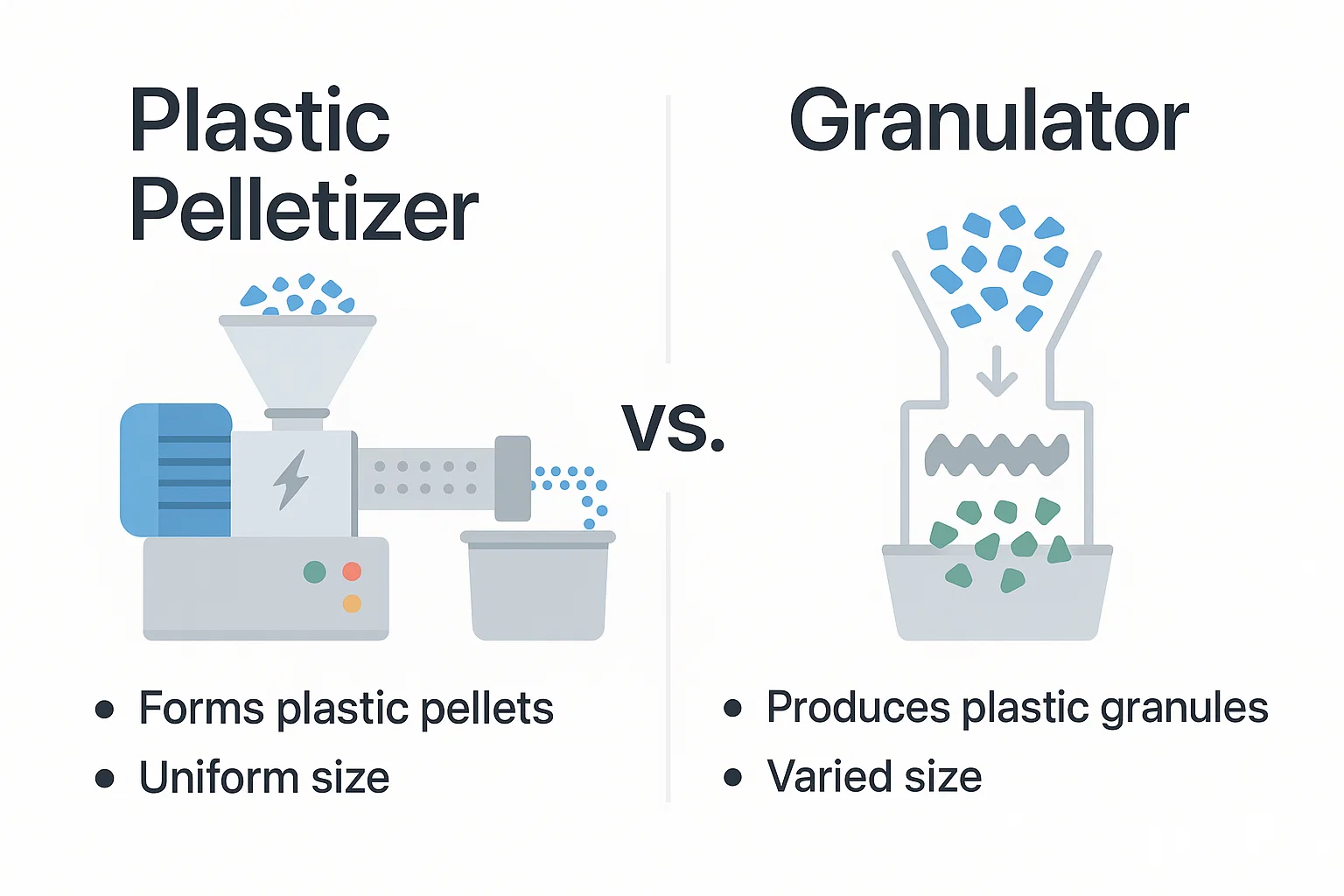
[18] No mundo do reciclagem industrial de plástico, a precisão e a eficiência são fundamentais. A capacidade de transformar resíduos plásticos em materiais recicláveis de alta qualidade depende da utilização da maquinaria adequada para cada tarefa específica. Dois equipamentos que são fundamentais para este processo, mas frequentemente confundidos, são o [20] e o granulador. Embora ambos estejam envolvidos na redução de tamanho, suas funções, processos e os produtos finais que eles criam são distintamente diferentes. pelotizador avançado [21] Para compradores de equipamentos de reciclagem industrial, engenheiros e profissionais do setor, entender esta diferença não é apenas uma questão de semântica; é crucial para projetar linhas de reciclagem eficientes, garantir a qualidade do plástico reciclado final e, finalmente, para tomar decisões de investimento informadas. Na Energycle, acreditamos em dotar nossos clientes do conhecimento necessário para escolher a melhor maquinaria de reciclagem de plástico para suas necessidades. Este artigo fornecerá uma visão geral completa das principais diferenças entre um granulador e um pelletizer.
[22] A Diferença Central: Líquido vs. Sólido
[23] A diferença mais fundamental entre um pelletizer e um granulador reside no estado do plástico que eles processam.
[25] Pelletizador de Plástico
-
A [26] Funciona com [27] plástico derretido. Sua função principal é cortar as fitas plásticas extrudidas em pelotas uniformes e de tamanho consistente. Este processo ocorre geralmente após o plástico ter sido lavado, despedaçado e derretido em um extrusor. [30] Granulador [31] , por outro lado, processa [32] plástico sólido. Ele é projetado para receber itens plásticos maiores, como partes rejeitadas, suportes ou corpos de fundição de processos de fabricação, e moerlos em fragmentos ou grânulos de tamanho irregular. [34] Esta distinção central influencia todos os outros aspectos de seu design, aplicação e papel no fluxo de trabalho de reciclagem.
-
A [35] Uma Visão mais Detalhada do Pelletizador de Plástico, on the other hand, processes solid plastic. It is designed to take larger plastic items, such as rejected parts, sprues, or runners from manufacturing processes, and grind them into smaller, irregular-sized flakes or granules.
This core distinction influences every other aspect of their design, application, and the role they play in a recycling workflow.
A Closer Look at the Plastic Pelletizer
A pelotizador avançado É um equipamento sofisticado que desempenha um papel vital na produção de grânulos de plástico reciclado de alta qualidade, prontos para o mercado. A uniformidade desses grânulos em termos de tamanho e forma é crucial para seu uso subsequente na manufatura de novos produtos plásticos, pois garante características de derretimento e fluxo consistentes em máquinas de injeção ou extrusão.
Como Funciona um Pelotizador de Plástico:
O processo de pelotização geralmente segue estes passos:
-
Extrusão: Plástico limpo e derretido é forçado através de uma cabeça de die, emergindo como cordas contínuas, semelhantes a esparguete.
-
Resfriamento: Essas cordas são então resfriadas, frequentemente em um banho de água ou através de um fluxo de ar, para solidificá-las.
-
Corte: As cordas resfriadas são alimentadas para o pelotizador, onde um conjunto de facas rotativas as corta em grânulos curtos e uniformes.
O resultado é um material bruto de alta densidade, fácil de transportar, com excelentes propriedades de manuseio.
Tipos de Pelotizadores de Plástico:
Existem vários tipos de pelotizadores de plástico, cada um adequado para diferentes aplicações e tipos de polímeros:
-
Pelotizadores de Corda: O tipo mais comum, ideal para uma ampla gama de termoplásticos.
-
Pelotizadores Submersos: O processo de corte ocorre submerso, o que é particularmente adequado para o processamento de termoplásticos como PET e PLA, pois a água resfria rapidamente e solidifica os grânulos.
-
Pelletizadores com Anel de Água: Uma cabeça de corte rotativa corta o polímero derretido ao sair do bico, e um anel de água imediatamente resfria e transporta os grânulos.
-
Pelletizadores com Refrigeração a Ar: Usados para polímeros sensíveis à água ou quando um conteúdo de umidade muito baixo é requerido.
Entendendo o Papel do Granulador
Um granulador é frequentemente uma das primeiras etapas no processo de reciclagem de plásticos rígidos. Sua função primária é decompor o lixo plástico volumoso em um insumo mais gerenciável e de tamanho consistente para processamento adicional.
Como Funciona um Granulador:
Um granulador utiliza uma série de lâminas rotativas e estáticas dentro de uma câmara de corte. O lixo plástico é alimentado para a câmara, onde a ação de剪切 a alta velocidade das lâminas tritura o material contra uma grade com buracos de tamanho específico. Os flocos ou grânulos resultantes passam pela grade quando alcançam o tamanho desejado.
Aplicações para Granuladores:
Granuladores são versáteis e podem ser usados para uma ampla gama de aplicações, incluindo:
-
Reciclagem In-House: Triturar sprues, runners e peças rejeitadas dos processos de injeção e moldagem por sopro para reuso imediato.
-
Resíduos Pós-Consumidor: Processar itens como garrafas plásticas, recipientes e perfis em flocos para lavagem e subsequente pelletização.
-
Preparando Material para Shredders: Em alguns casos, um granulador pode ser utilizado após um esmagador para alcançar um tamanho de partícula mais fino e mais uniforme.
Pelotizador vs. Granulador: Uma Comparação Head-to-Head
Para esclarecer melhor a distinção, aqui está uma comparação direta das duas máquinas:
| Recursos | [26] Funciona com [27] plástico derretido. Sua função principal é cortar as fitas plásticas extrudidas em pelotas uniformes e de tamanho consistente. Este processo ocorre geralmente após o plástico ter sido lavado, despedaçado e derretido em um extrusor. | Granulador |
| - | - | - |
| Material de Entrada | Fios de plástico derretido | Artigos de plástico sólido (por exemplo, rejeitados, sucata)
| Função Primária | Cria pellets uniformes a partir de plástico fundido | Tritura plástico sólido em grânulos/flocos mais pequenos
| Saída | Granulados consistentes e de alta densidade
| Processo | Corte de cordões extrudidos arrefecidos | Trituração e corte a alta velocidade de plástico sólido
| Posição na Linha de Reciclagem | Normalmente no final, após a extrusão | Frequentemente no início para a redução inicial do tamanho
| Vantagem Chave | Produz um produto de alta qualidade e pronto a ser comercializado | Reduz eficazmente o volume de resíduos plásticos volumosos
Diagrama de Fluxo de Trabalho: A Jornada da Reciclagem
gráfico TD
A[Recolha de resíduos de plástico] --> B{Triagem inicial};
B --> C[Trituração / Granulação];
C --> D{Lavagem e Limpeza};
D --> E[Secagem];
E --> F[Extrusão e fusão];
F --> G(Peletizador de plástico);
G --> H[Pellets finais para fabrico];
Escolha Correta para a Sua Aplicação
Para profissionais da indústria de reciclagem, a escolha entre um pelotizador e um granulador é determinada pelas necessidades específicas de sua operação.
-
Se seu objetivo é produzir um material bruto de alta qualidade e uniforme para venda ou uso direto na manufatura de novos produtos, um pelotizador avançado é essencial.
-
Se você está lidando com resíduos plásticos volumosos de linhas de produção ou resíduos pós-consumo que precisam ser quebrados para processamento adicional, um granulador é a escolha apropriada.
Em muitas plantas de reciclagem completas, ambos os equipamentos desempenham um papel crucial em uma solução de reciclagem completa e de ponta a ponta.
Na Energycle, especializamos-nos em fornecer maquinaria de reciclagem de plástico de alta performance e confiável, incluindo uma ampla gama de pelotizadores de plástico e granuladores. Nosso time de especialistas está à disposição para oferecer orientação e suporte, garantindo que você invista em equipamentos que proporcionarão os melhores resultados para suas necessidades específicas. Entre em contato conosco hoje para saber mais sobre nossas soluções inovadoras e como podemos ajudar a melhorar suas operações de reciclagem.