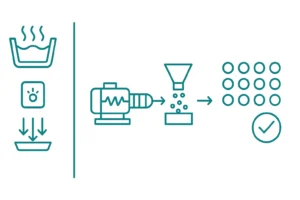
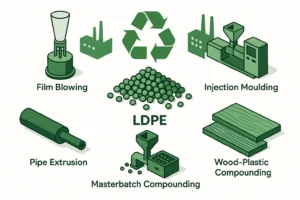
Recycling LDPE/LLDPE Films: Why You Need a Specialized Extruder
Why Soft Plastic Film Cannot Be Fed Into a Standard Extruder If you recycle LDPE/LLDPE film, shopping bags, stretch film, agricultural film, or woven bags, the most common issue is simple: the extruder cannot be fed consistently. In most cases, the root cause is not the extruder itself. It is the physical behavior of soft …