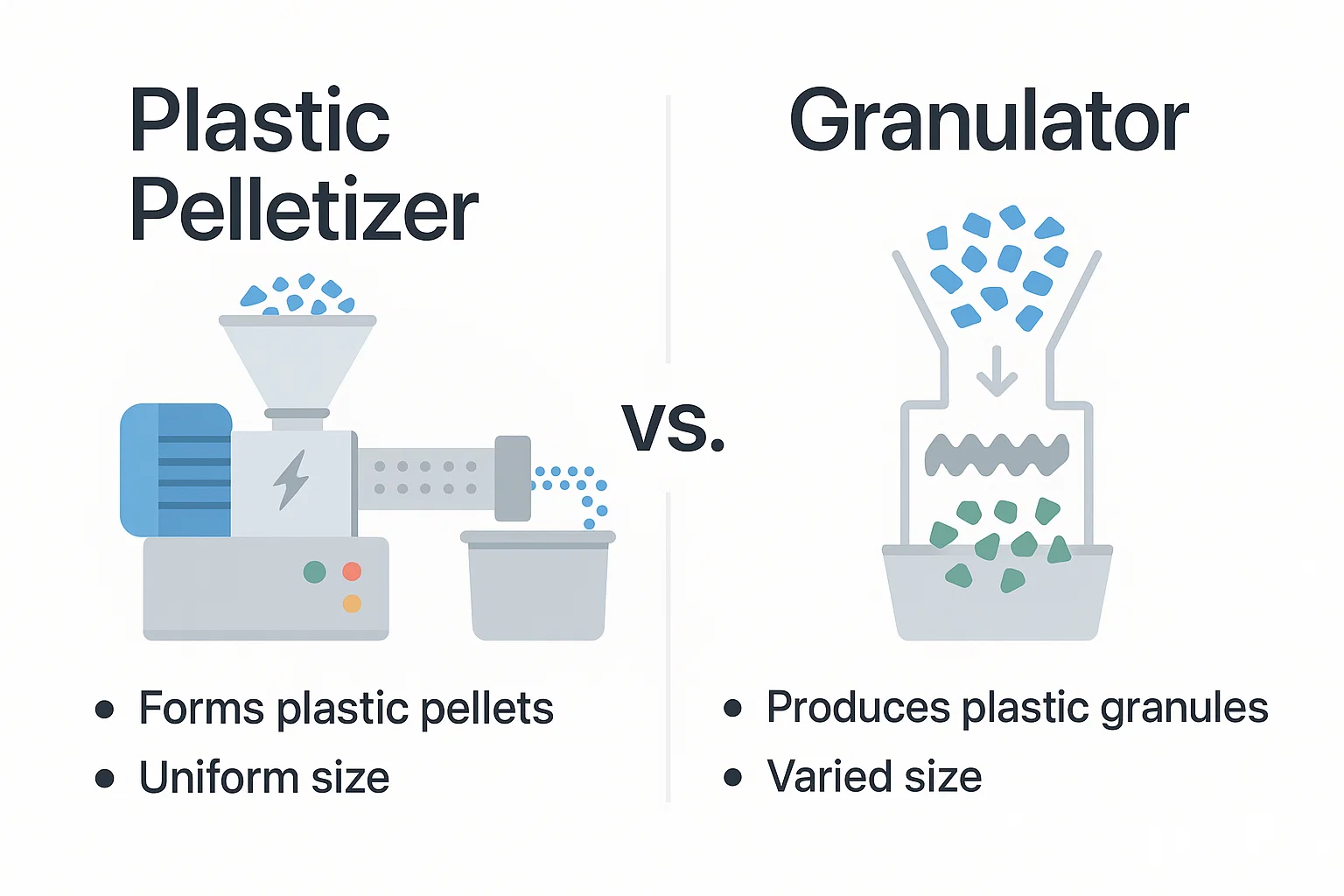
In the world of industrial plastic recycling, precision and efficiency are paramount. The ability to transform plastic waste into high-quality, reusable materials hinges on employing the right machinery for each specific task. Two pieces of equipment that are fundamental to this process, yet often confused, are the plastic pelletizer and the granulator. While both are involved in size reduction, their functions, processes, and the final products they create are distinctly different.
For industrial recycling equipment buyers, engineers, and professionals in the sector, understanding this difference is not just a matter of semantics; it is crucial for designing efficient recycling lines, ensuring the quality of the final recycled plastic, and ultimately, for making sound investment decisions. At Energycle, we believe in empowering our clients with the knowledge to select the best plastic recycling machinery for their needs. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of the key distinctions between a pelletizer and a granulator.
The Core Difference: Molten vs. Solid
The most fundamental difference between a pelletizer and a granulator lies in the state of the plastic they process.
-
A Plastic Pelletizer works with molten plastic. Its primary role is to take extruded plastic strands and cut them into uniform, consistently sized pellets. This process typically occurs after the plastic has been washed, shredded, and melted in an extruder.
-
A granulator, on the other hand, processes solid plastic. It is designed to take larger plastic items, such as rejected parts, sprues, or runners from manufacturing processes, and grind them into smaller, irregular-sized flakes or granules.
This core distinction influences every other aspect of their design, application, and the role they play in a recycling workflow.
A Closer Look at the Plastic Pelletizer
A plastic pelletizer is a sophisticated piece of equipment that plays a vital role in producing high-quality, market-ready recycled plastic pellets. The uniformity of these pellets in terms of size and shape is crucial for their subsequent use in manufacturing new plastic products, as it ensures consistent melting and flow characteristics in injection molding or extrusion machines.
How a Plastic Pelletizer Works:
The pelletizing process generally follows these steps:
-
Extrusion: Clean, molten plastic is forced through a die head, emerging as continuous strands, similar to spaghetti.
-
Cooling: These strands are then cooled, often in a water bath or through a current of air, to solidify them.
-
Cutting: The cooled strands are fed into the pelletizer, where a set of rotating knives cut them into short, uniform pellets.
The result is a high-density, easily transportable raw material with excellent handling properties.
Types of Plastic Pelletizers:
There are several types of plastic pelletizers, each suited to different applications and polymer types:
-
Strand Pelletizers: The most common type, ideal for a wide range of thermoplastics.
-
Underwater Pelletizers: The cutting process occurs underwater, which is particularly suitable for processing thermoplastics like PET and PLA, as the water rapidly cools and solidifies the pellets.
-
Water-Ring Pelletizers: A rotating cutting head slices the molten polymer as it exits the die, and a ring of water immediately cools and transports the pellets.
-
Air-Cooled Pelletizers: Used for water-sensitive polymers or when a very low moisture content is required.
Understanding the Granulator’s Role
A granulator is often one of the first steps in the recycling process for rigid plastics. Its primary function is to break down bulky plastic waste into a more manageable and consistently sized feedstock for further processing.
How a Granulator Works:
A granulator utilizes a series of rotating and stationary blades within a cutting chamber. Plastic waste is fed into the chamber, where the high-speed shearing action of the blades grinds the material against a screen with specific-sized holes. The resulting flakes or granules pass through the screen once they have reached the desired size.
Applications for Granulators:
Granulators are versatile and can be used for a wide range of applications, including:
-
In-house Recycling: Grinding down sprues, runners, and rejected parts from injection molding and blow molding processes for immediate reuse.
-
Post-Consumer Waste: Processing items like plastic bottles, containers, and profiles into flakes for washing and subsequent pelletizing.
-
Preparing Material for Shredders: In some cases, a granulator might be used after a shredder to achieve a finer and more uniform particle size.
Pelletizer vs. Granulator: A Head-to-Head Comparison
To further clarify the distinction, here is a direct comparison of the two machines:
| Feature | Plastic Pelletizer | Granulator |
| — | — | — |
| Input Material | Molten plastic strands | Solid plastic items (e.g., rejects, scrap) |
| Primary Function | Creates uniform pellets from molten plastic | Grinds solid plastic into smaller granules/flakes |
| Output | Consistent, high-density pellets | Irregularly shaped granules or flakes |
| Process | Cutting of cooled, extruded strands | High-speed grinding and shearing of solid plastic |
| Position in Recycling Line | Typically at the end, after extrusion | Often at the beginning for initial size reduction |
| Key Advantage | Produces a high-quality, market-ready product | Efficiently reduces the volume of bulky plastic waste |
Workflow Diagram: The Recycling Journey
graph TD
A[Plastic Waste Collection] --> B{Initial Sorting};
B --> C[Shredding / Granulating];
C --> D{Washing and Cleaning};
D --> E[Drying];
E --> F[Extrusion and Melting];
F --> G(Plastic Pelletizer);
G --> H[Final Pellets for Manufacturing];
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
For professionals in the recycling industry, the choice between a pelletizer and a granulator is determined by the specific requirements of their operation.
-
If your goal is to produce a high-quality, uniform raw material for sale or for direct use in manufacturing new products, a plastic pelletizer is essential.
-
If you are dealing with bulky plastic scrap from production lines or post-consumer waste that needs to be broken down for further processing, a granulator is the appropriate choice.
In many comprehensive recycling plants, both machines play a crucial role in a complete, end-to-end recycling solution.
At Energycle, we specialize in providing high-performance, reliable plastic recycling machinery, including a wide range of plastic pelletizers and granulators. Our team of experts is on hand to offer guidance and support, ensuring you invest in the equipment that will deliver the best results for your specific needs. Contact us today to learn more about our innovative solutions and how we can help you enhance your recycling operations.