An Expert Guide to Recycling Post-Industrial BOPP Film Scrap
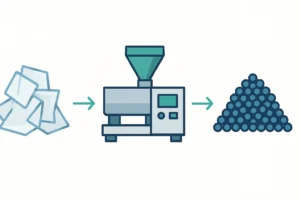
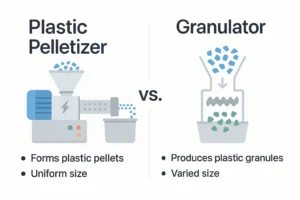
Post-industrial BOPP film scrap is a valuable resource, not waste. This comprehensive guide details the step-by-step process for recycling BOPP film, highlighting the critical role of a specialized plastic pelletizing machine. Learn how to overcome common challenges and turn your factory scrap into high-quality, profitable pellets with expert insights from Rumtoo Machine.