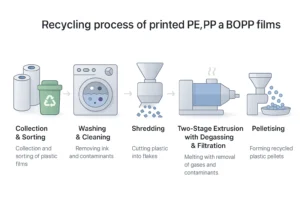
Efficient Recycling of Highly Printed PE, PP, and BOPP Films
Recycling highly printed PE, PP, and BOPP films requires advanced equipment to remove inks and contaminants. Learn how technologies like Repro-Flex Plus enable the production of high-quality recycled pellets for industrial reuse.